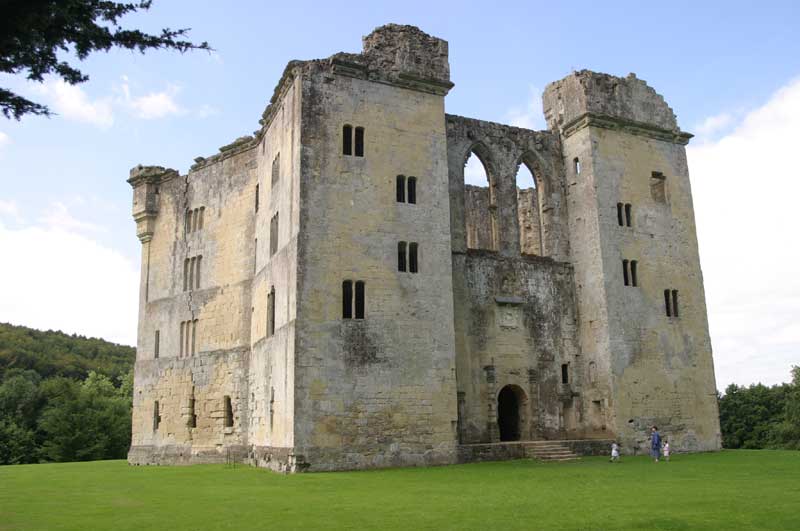
hortly after becoming King of England in 1066 William the Conqueror constructed an earth and timber castle in the corner of the old Roman city walls of London. Around this was dug a ditch and a bank was formed with a wooden palisade on top. From this point William could command London and monitor all ship movements up and down the river Thames. About ten years after the Conquest William decided to strengthen the castle. Gundulf the Bishop of Rochester, whose building techniques were admired by William, was brought to London to design and build the new keep. The foundations were laid in 1078 and the structure was completed in the reign of William Rufus in 1097. This is now known as the White Tower after Henry III whitewashed the exterior. The tower has walls fifteen feet thick at the base, a chapel dedicated to St John the Evangelist taking up two of the upper floors, a 40 foot deep well and more than one crypt. Building work again commenced in around 1189 when the chancellor of the time William Longchamp the Bishop of Ely ordered the enlargement of the bailey that surrounded the tower.
hortly after becoming King of England in 1066 William the Conqueror constructed an earth and timber castle in the corner of the old Roman city walls of London. Around this was dug a ditch and a bank was formed with a wooden palisade on top. From this point William could command London and monitor all ship movements up and down the river Thames. About ten years after the Conquest William decided to strengthen the castle. Gundulf the Bishop of Rochester, whose building techniques were admired by William, was brought to London to design and build the new keep. The foundations were laid in 1078 and the structure was completed in the reign of William Rufus in 1097. This is now known as the White Tower after Henry III whitewashed the exterior. The tower has walls fifteen feet thick at the base, a chapel dedicated to St John the Evangelist taking up two of the upper floors, a 40 foot deep well and more than one crypt. Building work again commenced in around 1189 when the chancellor of the time William Longchamp the Bishop of Ely ordered the enlargement of the bailey that surrounded the tower. When Henry III became King he began improving of the area of the castle between the Tower and the river by building the Wakefield and Lanthorn Towers. Henry used the Wakefield Tower, which is the second largest tower of the castle, as he own private residence. Between 1275 and 1285 Edward I spent large sums of money improving the fortifications. A new moat was dug and a curtain wall was built around it. The land between the Tower and the river was levelled and new apartments were built on the shore. Edward had a complex of gates added which meant it was extremely difficult to attack the castle through the main land entrance.